INTRODUCTION
Have you ever heard of fibroids? You might be surprised to know that nearly 70–80% of women develop fibroids at some point in their lives — but most don’t even realize it. Fibroids are one of the most common reasons for heavy periods, pelvic pain, and even fertility issues, yet they’re rarely talked about openly.
In this blog, we’ll uncover what fibroids really are, separate myths from facts, and explore the latest treatments and lifestyle tips to empower women with knowledge.
What Are Fibroids?
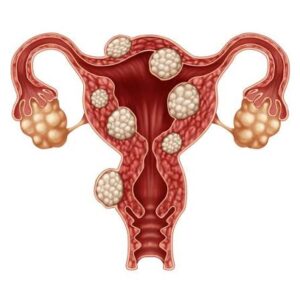
Fibroids, also called uterine leiomyomas, are non-cancerous growths that develop in or around the uterus. They vary in size — some are as tiny as a seed, while others can grow as large as a grapefruit.
There are different types:
- Intramural fibroids – grow inside the uterine wall (most common).
- Submucosal fibroids – grow into the uterine cavity, may affect fertility.
- Subserosal fibroids – grow outside the uterus, sometimes pressing on other organs.
- Pedunculated fibroids – attached by a stalk-like structure.
- Important: Fibroids are not cancerous, and having them does not mean you’re at a higher risk for uterine cancer.
Common Symptoms
Some women have no symptoms, while others may face:
- Heavy or prolonged periods (leading to anemia)
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- Frequent urination (if fibroids press on the bladder)
- Constipation or back pain
- Bloating or abdominal swelling
- Fertility problems or repeated miscarriages (in some cases)
What Causes Fibroids?
The exact cause is still unknown, but research shows:
- Hormones (Estrogen & Progesterone): These hormones promote fibroid growth.
- Genetics: If your mother or sister had fibroids, you’re more likely to develop them.
- Age: Common between 30–50 years old.
- Lifestyle Factors: Obesity, high-stress levels, and poor diet may increase risk.
Complications
In some women, untreated fibroids may lead to:
- Severe anemia (from excessive blood loss)
- Pregnancy complications such as preterm birth
- Infertility (if fibroids block the fallopian tubes or distort the uterus)
Facts Vs Myths
- Fibroids always turn into cancer. False – Fibroids are benign, and malignant transformation is extremely rare.
- Surgery is the only way to treat fibroids. False – Medications and minimally invasive procedures can shrink fibroids.
- Only older women get fibroids. False – Women in their 20s and 30s can also have fibroids.
- Fibroids mean you can’t get pregnant. False – Many women with fibroids conceive naturally and have healthy pregnancies.
- Fibroids always need to be removed. False – If small and symptom-free, doctors usually just monitor them.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on size, symptoms, and future pregnancy plans:
- Watchful Waiting: If there are no symptoms, regular check-ups are enough.
- Medications: Hormonal therapy (like GnRH agonists), pain relievers, or iron supplements for anemia.
- Non-Surgical Procedures:
- Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE): Cuts off blood supply to shrink fibroids.
- MRI-guided focused ultrasound: Uses sound waves to destroy fibroids.
Surgical Options:
- Myomectomy: Removes fibroids but preserves the uterus.
- Hysterectomy: Removes the uterus (only for severe cases where other treatments fail).
Lifestyle & Prevention Tips
While fibroids can’t always be prevented, healthy habits can lower risk and improve symptoms:
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Eat more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Reduce red meat and processed foods.
- Manage stress with yoga, meditation, or exercise.
- Get regular pelvic check-ups to catch fibroids early.
Empowering Women
Fibroids can be scary — but knowledge is power. Don’t ignore heavy periods, constant bloating, or pelvic pain. Keeping a menstrual diary and consulting a gynecologist early can make a big difference.
Talking openly about fibroids also helps break the stigma around women’s reproductive health and encourages more women to seek timely care.
Conclusion
Fibroids are common, but they don’t have to control your life. With the right knowledge, treatment, and support, you can manage symptoms and live a healthy, empowered life.
If you found this article helpful, share it with your friends and family — you never know who might need this information!


 x carbohydrate and fibre to balance blood sugar.
x carbohydrate and fibre to balance blood sugar.