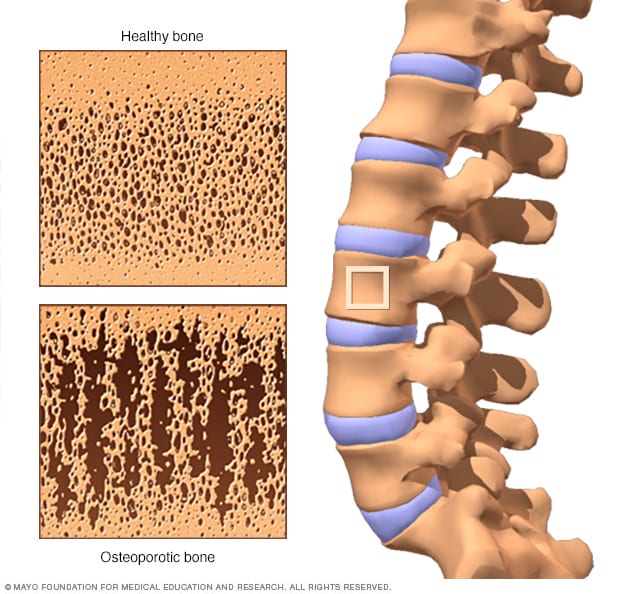
Osteoporosis is a condition where bones become weak and fragile, increasing the risk of fractures. It often develops silently and is most common in older adults, especially women. Nutrition plays a key role in both prevention and management of this disease.
Calcium and vitamin D are the two most important nutrients for strong bones. Dairy products, leafy green vegetables, almonds, and fortified foods are excellent sources of calcium. Vitamin D, obtained from sunlight, fish, and eggs, helps the body absorb calcium effectively.
Protein, magnesium, and vitamin K also support bone strength, while excess caffeine, soft drinks, and high salt intake can weaken bones. Maintaining a healthy weight, staying active with weight-bearing exercises, and eating balanced meals are essential strategies.
Good nutrition not only slows bone loss but also reduces fracture risk. A diet rich in bone-friendly nutrients truly builds a stronger foundation for lifelong health.