Introduction
- Myasthenia Gravis can be confusing.
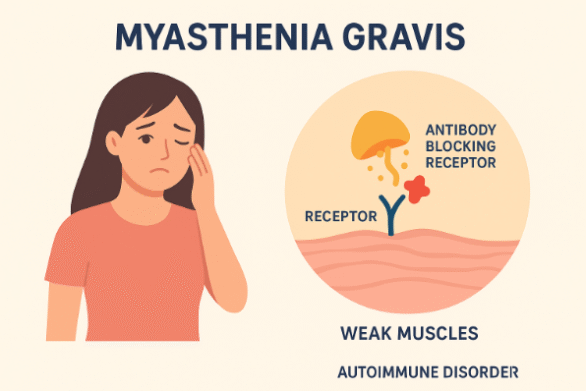
- Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disease that causes muscle weakness by interrupting the signaling between your nerves and muscle.
In this post you will find:
- What Myasthenia Gravis is?
- What causes myasthenia gravis and potential triggers or factors for worsening?
- Key signs and symptoms to know or be aware of?
- How myasthenia gravis is diagnosed and treated?
- Some simple ideas for living well when you have myasthenia gravis?
1. What is Myasthenia Gravis?
- Myasthenia Gravis is a long-standing condition in which the immune system interferes with the communication between the nerves and the muscles.
- You can use an analogy about Wi-Fi, with the brain signal being weak or intermittent, causing the muscles to be tired and weak.
2. Causes of Myasthenia Gravis
The specific cause of MG is not always identified, but the most common causes are:
- Immune system attack — the body produces antibodies that block muscle receptors (acetylcholine receptors).
The specific cause of MG is not always identified, but the most common causes are:
- Issues with the thymus — usually enlarged or have tumors (thymomas).
- Role of inheritance — It can run in families but is rarely inherited.
- Common triggers — stress, infections, heat, fatigue, and some medications (antibiotics, beta-blockers, magnesium).
3. Signs and Symptoms of Myasthenia Gravis
Symptoms are highly variable, but muscle weakness is the primary characteristic and worsens with activity and improves after rest.
Common Symptoms:
- Eyes – Drooping eyelids (ptosis); double vision (diplopia).
- Face & mouth – Weak smile; difficulty chewing or speaking clearly.
- Swallowing – Trouble eating or choking on food.
- Muscles – Weakness in arms, legs, or neck (especially after activity).
- Breathing – Shortness of breath (with potential to progress to myasthenic crisis, an emergency).
4. How is Myasthenia Gravis Diagnosed?
Doctors use testing methods to confirm MG:
- Physical exam and checking for muscle fatigue issues.
- Blood testing – detects the antibodies associated with MG.
- Electromyography (called EMG) – tests how a nerve communicates with a muscle.
- CT or MRI testing for thymus gland abnormalities.
5. Myasthenia Gravis Treatment
While there’s currently no available cure, treatments can help alleviate symptoms so patients can lead a full life.
1. Medications:
- Pyridostigmine – Enhances communication between nerve endings and muscles.
- Steroids (such as prednisone) – Decreases the immune system’s attack.
- Immunosuppressants – Regulates the immune system.
2. Surgical Procedures:
- Thymectomy – Removal of the thymus gland may lessen symptoms in many cases.
3. Advanced Treatment (for severe cases):
- Plasmapheresis – Removes harmful antibodies from blood supply.
- Intravenous immunoglobulin (IV IG) – Provides “good” antibodies to body.
4. Everyday-advice:
- Rest several times throughout day between activities.
- Eat smaller, softer meals if easier to swallow.
- Use eye patch if double vision present.
- Avoid extreme heat, stress, infections.
- Keep in touch with support groups.
6. Life with Myasthenia Gravis
The bright side? Many people with MG lead a normal, active life. With proper treatment, healthy habits, and support from family and friends, MG does not have to interfere with your enjoyment of life.
7. FAQs About Myasthenia Gravis
1. Can you cure Myasthenia Gravis?
Not at this time, but you can manage the symptoms with treatment.
2. Who gets Myasthenia Gravis?
Myasthenia gravis can affect anyone. However, it is most common in women under 40 and men over 60.
3. Can I exercise?
Yes, gentle light activity should be fine. You do not want to push yourself to the detriment of your health.
4. What is a Myasthenic Crisis?
This refers to the respiratory muscles being too weak to provide adequate ventilation, thereby causing marked shortness of breath. This situation qualifies as a medical emergency.
8. Key Takeaways:
- Myasthenia Gravis is characterized by muscle weakness due to the ineffective communication that occurs between nerves and muscles.
- Symptoms include droopy eyelids, double vision, difficulty swallowing, and problems with breathing.
- Treatment options include medications, surgical procedures, and supportive therapies.
- Although living with MG requires accommodations/different approaches, it is still possible to live active and fulfilling lives with proper treatment.
9. SAMPLE ONE-DAY MEAL PLAN
Breakfast
- Soft scrambled eggs with spinach (protein + iron)
- 1 slice soft whole wheat bread with butter.
- Banana smoothie (with milk/yogurt).
Mid-Morning Snack
- Yogurt with mashed berries.
- Soft oatmeal cookie.
Lunch
- Soft cooked khichdi (rice + lentils) with vegetables.
- Boneless fish or chicken cooked till tender.
- Stewed apples or pears.
Evening Snack
- Rice pudding (kheer) or custard.
- Herbal tea (decaf if sensitive).
Dinner
- Mashed sweet potato with soft lentils.
- Steamed soft vegetables (zucchini, pumpkin, carrots).
- Minced chicken or tofu curry (mildly spiced).
Bedtime Snack
- Warm milk with turmeric or honey.
- 2 soaked dates (easy to chew and energy-giving).
10. Foods to Limit/Avoid
- Dry, crumbly foods (crackers, dry bread).
- Tough meats (beef, mutton unless minced and well-cooked).
- Sticky foods (peanut butter, chewy candies).
- Excess caffeine (can worsen weakness).
- Overly spicy or acidic foods (may irritate throat).
Final Thought: Myasthenia Gravis may be rare, but with the right care and awareness, people living with MG can lead strong, confident, and happy lives.