🌿 Understanding Hepatitis C: Causes, Risks, Prevention, and Recovery:
Hepatitis C is a serious liver disease caused by the Hepatitis C virus (HCV). Unlike some other forms of hepatitis, Hepatitis C is often chronic, meaning it can last a lifetime and lead to severe liver damage, including cirrhosis, liver cancer, or even liver failure. But with early detection and the right treatment, Hepatitis C is now curable in most people.
❓ Why Hepatitis C Happens
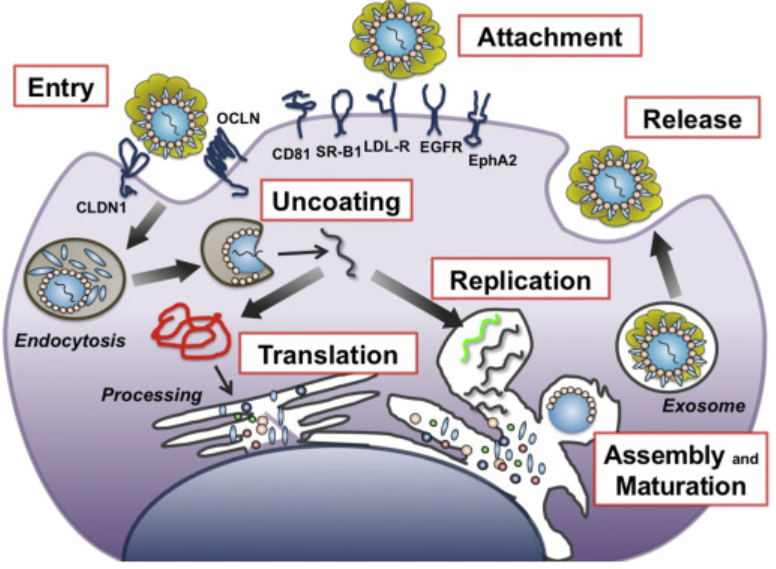
Hepatitis C occurs when the Hepatitis C virus infects liver cells. The virus enters the body, usually through blood-to-blood contact, and begins to attack liver tissue. Over time, this causes inflammation, scarring, and damage.
Unlike Hepatitis A or B, there is no vaccine for Hepatitis C, making prevention and awareness even more important.
🔍 How Hepatitis C Happens
Hepatitis C is spread primarily through exposure to infected blood. Common transmission routes include:
-
Sharing needles or syringes (IV drug use)
-
Blood transfusions before 1992 (before widespread HCV screening)
-
Unsafe or unsterile tattooing or piercing
-
Accidental needle sticks in healthcare settings
-
From mother to baby during childbirth (less common)
-
Sharing personal items like razors or toothbrushes (rare)
It is not typically spread through casual contact, kissing, coughing, or sharing food and drinks.
⚠️ Diseases Caused by Hepatitis C
Chronic Hepatitis C can cause a range of serious health complications:
-
Chronic Liver Disease
-
Cirrhosis (liver scarring)
-
Liver Failure
-
Liver Cancer (Hepatocellular Carcinoma)
-
Cryoglobulinemia (immune complex disorder)
-
Glomerulonephritis (kidney damage)
-
Type 2 Diabetes (linked to liver dysfunction)
-
Fatty Liver Disease
🧓 Who Is at Risk? Age and Health Conditions
Certain individuals are at higher risk for Hepatitis C:
Age Groups:
-
People born between 1945 and 1965 (baby boomers): higher rates due to lack of early screening
-
Anyone who received a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992
Health Conditions and Risk Factors:
-
People with HIV
-
People who inject drugs or have a history of IV drug use
-
Individuals on hemodialysis
-
Healthcare workers exposed to blood
-
Infants born to HCV-positive mothers
-
People with unregulated tattoos or piercings
💊 Sources to Recover from Hepatitis C
The good news is that Hepatitis C is curable in most cases with proper treatment. Recovery sources include:
1. Antiviral Medications (DAAs)
Direct-Acting Antivirals (DAAs) are highly effective and can cure 95% or more of cases. Common regimens include:
-
Sofosbuvir
-
Ledipasvir
-
Velpatasvir
-
Glecaprevir/pibrentasvir
Treatment duration is usually 8 to 12 weeks.
2. Regular Monitoring
-
Liver function tests
-
Viral load testing
-
Ultrasounds or fibroscans to monitor liver damage
3. Liver Transplant (in advanced cases)
For people with end-stage liver disease or liver cancer, transplant may be necessary.
🌱 Natural Sources for Supportive Recovery
While natural remedies cannot cure Hepatitis C, they can support liver health during and after treatment:
Liver-Supportive Foods:
-
Leafy greens (spinach, kale)
-
Garlic (natural detoxifier)
-
Beetroot (supports liver enzyme activity)
-
Turmeric (anti-inflammatory and antioxidant)
-
Avocados (rich in healthy fats)
Herbs (use only with medical advice):
-
Milk thistle (supports liver repair)
-
Dandelion root (aids digestion and detox)
-
Licorice root (anti-inflammatory)
Lifestyle Support:
-
Hydration (helps flush toxins)
-
Avoid alcohol and drugs toxic to the liver
-
Regular exercise to maintain healthy weight
🛡️ Tips to Prevent Hepatitis C
Prevention is key since no vaccine exists yet:
-
Avoid sharing needles or syringes
-
Use only licensed, clean tattoo/piercing studios
-
Practice safe sex, especially with multiple partners
-
Avoid sharing personal items like razors or toothbrushes
-
Wear gloves when handling blood or open wounds
-
Healthcare workers should follow all safety protocols
-
Get tested if you are at high risk
🚨 Common Symptoms of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is often called a “silent” infection because many people don’t notice symptoms for years. When symptoms do occur, they may include:
-
Fatigue
-
Nausea or vomiting
-
Abdominal pain (especially upper right side)
-
Jaundice (yellow skin and eyes)
-
Dark urine
-
Pale stool
-
Loss of appetite
-
Joint pain
-
Confusion or brain fog (in later stages)
🧪 How Is Hepatitis C Diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a blood test to detect the virus:
-
HCV Antibody Test – Shows if you’ve ever been exposed
-
HCV RNA Test – Confirms current infection
-
Genotype Test – Identifies HCV strain (to tailor treatment)
-
Liver tests/imaging – To assess damage (ALT, AST, fibroscan)
🧠 Mental and Emotional Health with Hepatitis C
Chronic illness can affect your mental health. It’s normal to feel overwhelmed or anxious after diagnosis. Support options include:
-
Talking to a counselor or therapist
-
Joining a Hepatitis C support group
-
Educating yourself to reduce fear
📝 Final Thoughts
Hepatitis C is a serious but treatable disease. With proper medical treatment, healthy lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring, people with Hepatitis C can live long, healthy lives.
Stay aware, get tested if you’re at risk, and always practice safe habits to protect your liver and overall health.
✅ Quick Recap Checklist:
-
✅ Know your risk
-
✅ Get tested if you think you were exposed
-
✅ Follow doctor-prescribed antiviral treatment
-
✅ Eat liver-supportive foods
-
✅ Avoid alcohol and harmful substances
-
✅ Take care of your emotional well-being