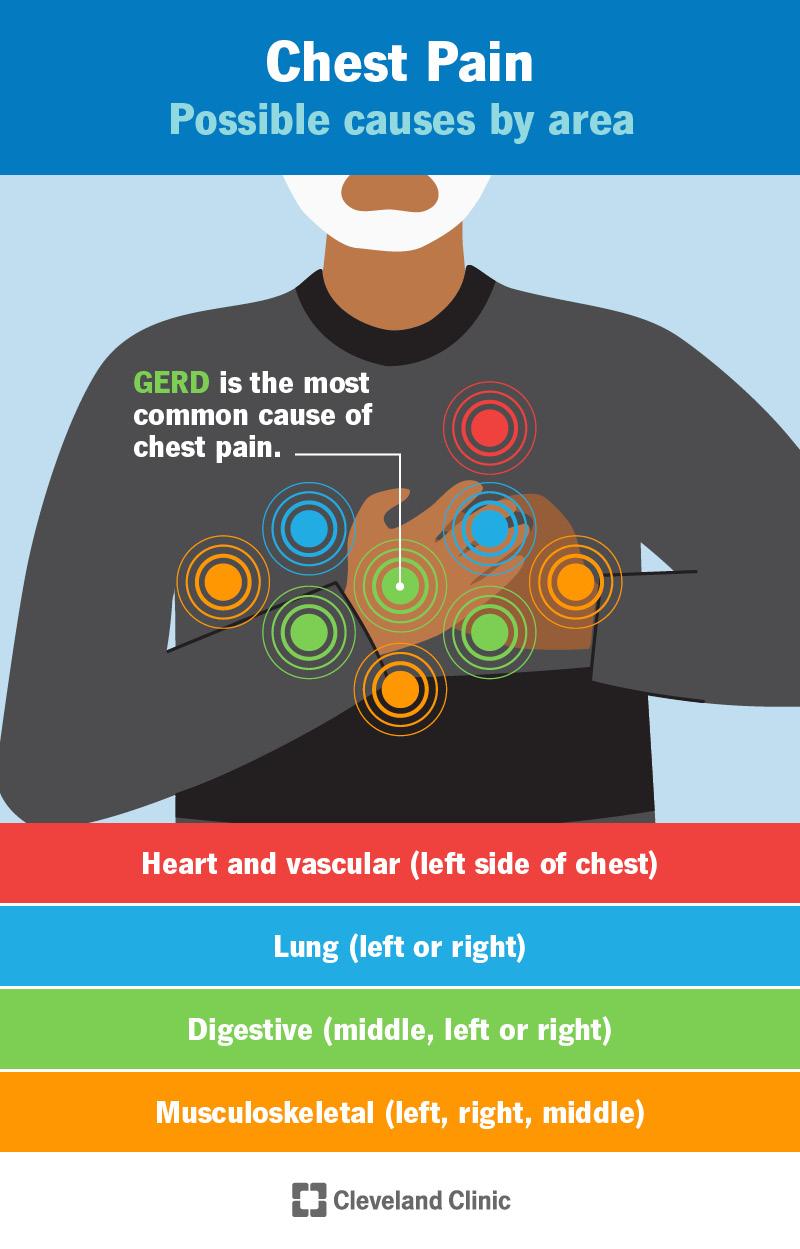
A heart attack, also known as a myocardial infarction, occurs when blood flow to the heart is suddenly blocked, usually due to the buildup of fatty deposits (plaque) in the coronary arteries, and this interruption can cause serious damage to the heart muscle. It is one of the leading causes of death worldwide, yet it is often preventable with timely awareness and healthy lifestyle choices. Common risk factors include smoking, unhealthy eating habits, high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, obesity, stress, and a sedentary lifestyle. Warning signs may appear suddenly or gradually, and they often include chest pain or pressure, pain radiating to the arm, neck, or jaw, shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, and extreme fatigue. In such cases, immediate medical help is critical, as early intervention can save lives. If a heart attack occurs, calling emergency services, keeping the person calm, and providing aspirin (if not allergic) until professional help arrives can make a difference. Prevention, however, is always better than cure — adopting a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, engaging in regular physical activity, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol, managing stress, and scheduling regular health checkups can greatly reduce the risk. By making small but consistent changes in daily habits, everyone can take control of their heart health and lower the chances of experiencing this life-threatening condition.