Dementia: Causes and Nutrition’s Role in Brain Health
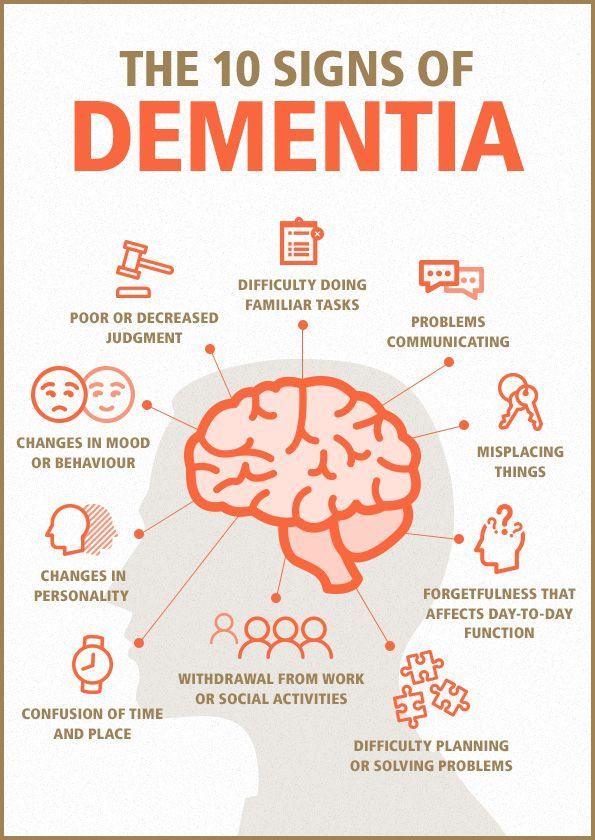
Dementia is a gradual decline in memory, reasoning, and behavior, most often affecting older adults. It develops when brain cells are damaged, commonly due to Alzheimer’s disease, stroke, head trauma, or other neurological conditions. Factors such as advancing age, genetics, hypertension, diabetes, and lifestyle habits can increase the likelihood of developing dementia.
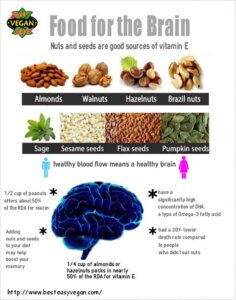
Nutrition has a powerful influence on brain function and may help slow cognitive decline. Diets rich in protective nutrients support memory and overall mental health. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds, aid communication between brain cells. Antioxidants like vitamins C and E, along with polyphenols from colorful fruits, vegetables, and green tea, defend against oxidative stress. B vitamins—especially B6, B12, and folate—reduce homocysteine, a compound linked to brain shrinkage. Additionally, vitamin D and magnesium play key roles in nerve and cognitive function.