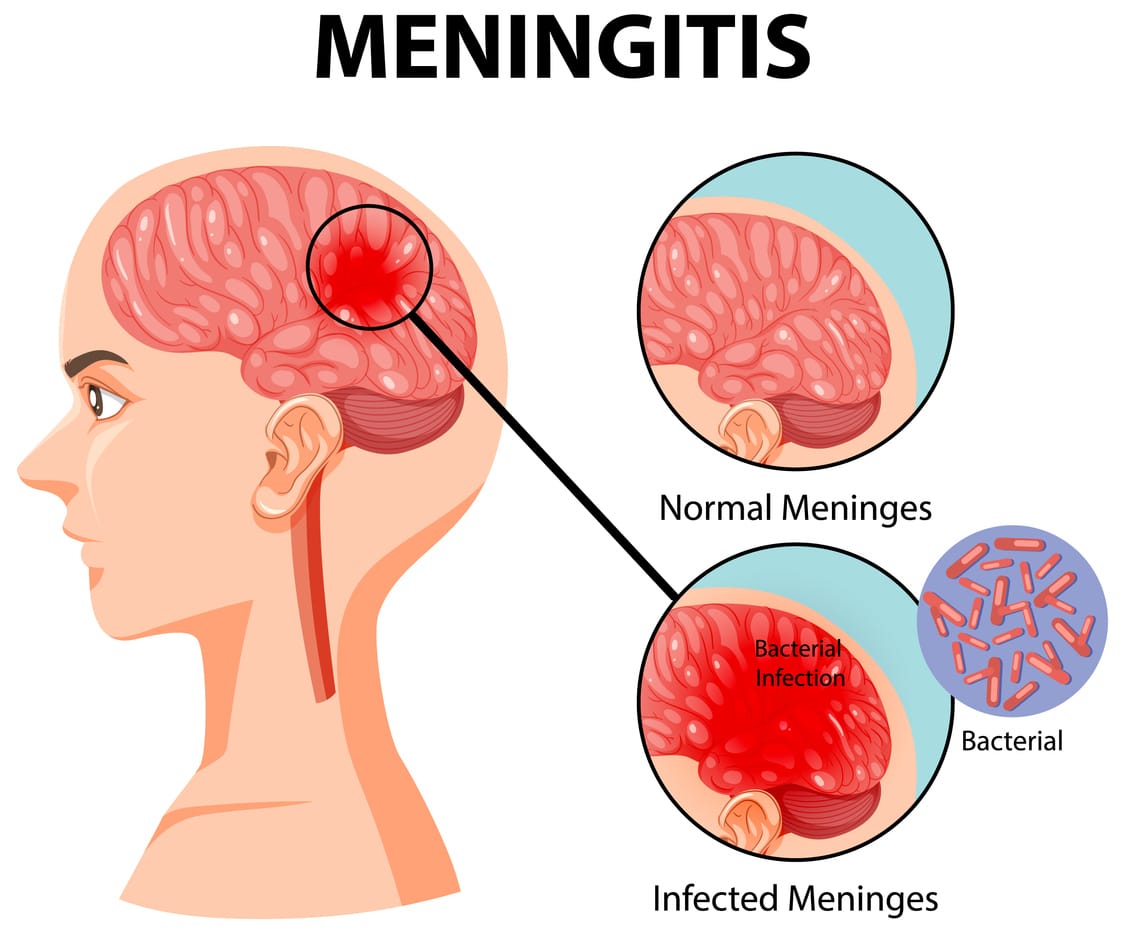
Acute spinal meningitis is an inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord ,caused primarily by bacterial or viral infections, it can progress rapidly, sometimes leading to brain damage or death within hours if untreated. While immediate medical care is essential, emerging research highlights nutrition’s critical role in supporting recovery, reducing inflammation, and enhancing immune defense.
Recognizing the Symptoms:
- In Adults: Severe headache, stiff neck, light sensitivity, fever, vomiting, seizures, and pain radiating from the spine.
- In Children: High-pitched crying, dislike of being touched, lethargy, refusal to eat, cold extremities, and pale or blotchy skin.
Causes and Risk Factors:
Spinal meningitis typically results from bacterial or viral infections. Risk factors include close contact with infected individuals, a weakened immune system, respiratory infections, or living in crowded environments.
Bacterial meningitis: Requires immediate IV antibiotics.
Viral meningitis: Often resolves with supportive care but still needs medical evaluation.
The Role of Nutrition in Recovery:
- Strengthening Immunity:
Vitamins A, C, D, E – support immune function and tissue repair.
Zinc – aids cellular repair.
Probiotics – maintain gut health and improve immune response. - Supporting Brain and Nervous System Health:
Omega-3 Fatty Acids – reduce neuroinflammation and support cognitive recovery.
B Vitamins (B6, B12, Folate) – promote nerve regeneration and brain function. - Managing Inflammation:
Include turmeric, berries, and leafy greens to naturally reduce inflammation. - Hydration and Electrolyte:
Replace fluids lost from fever or vomiting to maintain electrolyte balance. - Restoring Gut Health After Antibiotics
Consume probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables to rebuild gut flora.