The Importance of Brain Compression: Understanding the Concept and Its Application
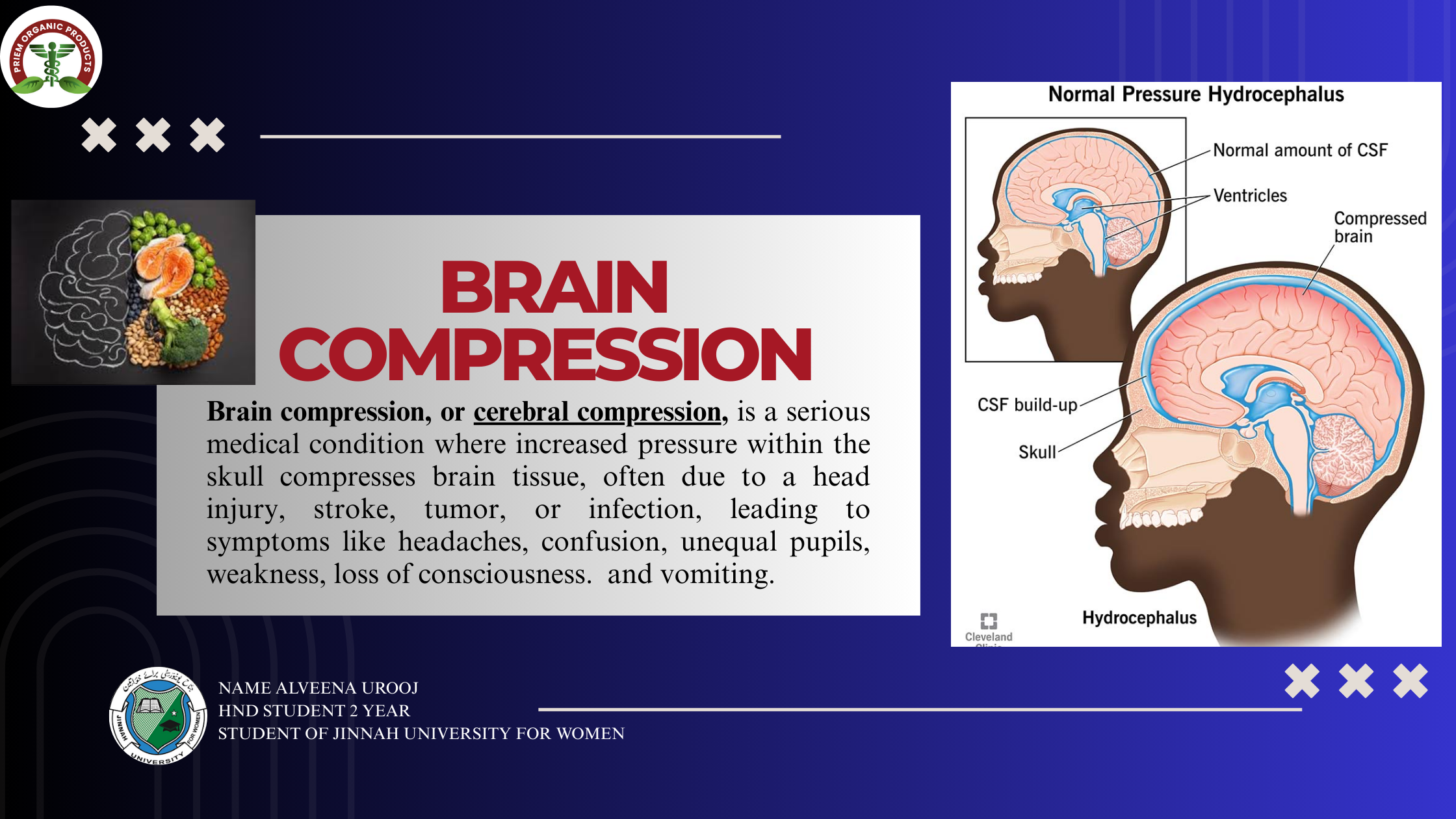
Brain compression, also known as cerebral compression, refers to the increased pressure on the brain due to various factors, including trauma, tumors, or other medical conditions. This compression can lead to serious complications, including brain damage, disability, and even death. In this blog, we will explore the concept of brain compression, its causes, symptoms, and diet.
Causes:
– Traumatic brain injury (TBI)
– Brain tumors
– Stroke or cerebral vasculature disorders
– Infections, such as meningitis or encephalitis
– Hydrocephalus (fluid accumulation in the brain)
Common Symptoms of Brain Compression
– Headache
– Confusion
– Dizziness
– Nausea and vomiting
– Weakness or numbness in limbs
– Vision problems
– Seizures
Nutritional Support for Recovery:
Foods to Include:
1. Fatty Fish: Salmon, sardines, and mackerel are rich in omega 3 fatty acids.
2. Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and collard greens are packed with antioxidants and magnesium.
3. Nuts and Seeds: Walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds are rich in omega 3 and antioxidants.
4. Fruits: Berries, citrus fruits, and apples are high in antioxidants.
5. Whole Grains: Brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat provide sustained energy and fiber.
Foods to Avoid
1. Processed Foods: Foods high in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats can exacerbate inflammation.
2. Food Additives: Some food additives, such as MSG and artificial sweeteners, may trigger adverse reactions.
3. Caffeine and Alcohol.
References
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- American Association of Neurological Surgeons (AANS)
- Mayo Clinic