Herpes zoster, commonly known as shingles, is a viral infection caused by the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus—the same virus responsible for chickenpox. After recovering from chickenpox, the virus remains dormant in nerve tissues and can reactivate later in life, often triggered by stress, aging, or a weakened immune system.
The hallmark symptom is a painful, blistering rash that usually appears on one side of the body or face, following the path of nerves. Before the rash develops, individuals may experience tingling, itching, or burning sensations. Other symptoms include fever, headache, and fatigue.
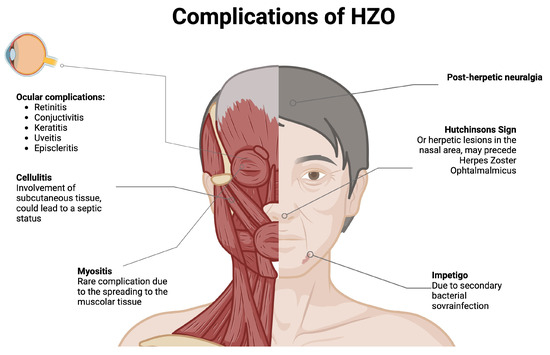
While shingles usually resolves within 2–4 weeks, complications such as postherpetic neuralgia (persistent nerve pain) can occur, especially in older adults. Early treatment with antiviral medications helps reduce severity and duration. Preventive measures, like the shingles vaccine, are highly recommended for adults over 50 to lower risk and protect long-term health.